The Liver: A to ZSD is devoted to liver health awareness related to peroxisomal biogenesis disorder-Zellweger spectrum disorder (PBD-ZSD). Free testing is available for eligible PBD-ZSD patients. Use the PBD-ZSD Liver Symptom Checker to help.
Understanding the liver
Hard at work to keep you healthy
The liver is part of your digestive system, and the largest internal organ in your body, tasked with over 500 jobs to help keep you healthy. The liver converts food into energy, cleans the blood, and removes waste from the body—just to name a few.
In order to do this, the liver secretes a yellowish-green fluid called bile to break down and absorb fats and other nutrients from the food we eat. Bile also helps eliminate excess cholesterol, bilirubin, and toxins from the body.
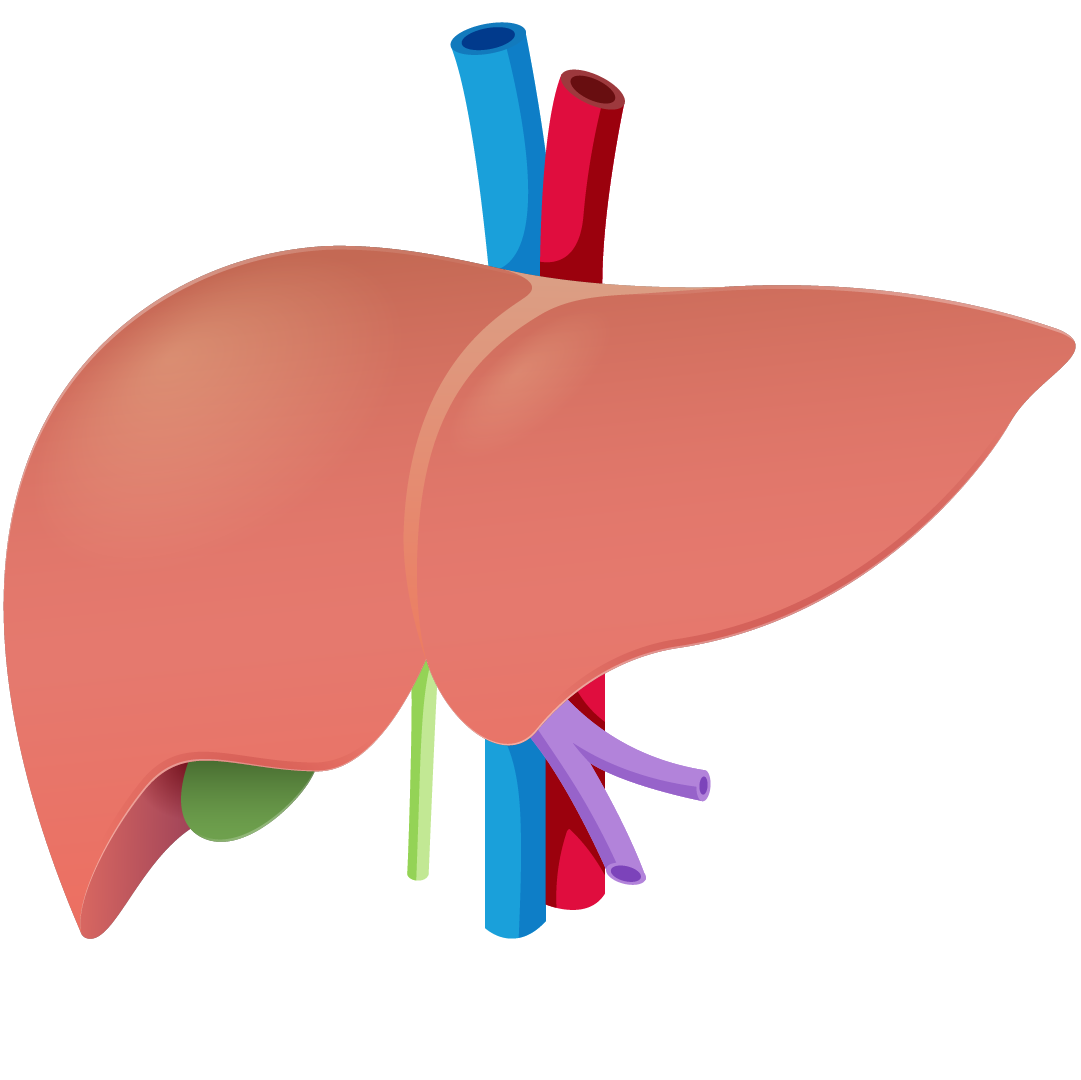

Some of the most important functions of the liver include:
- Producing bile and bile acids to help absorb fats and vitamins from the food you eat, which is important for growth and overall health
- Cleaning the blood of certain bacteria to prevent infections and help support the immune system
- Breaking down medicines into nontoxic forms that the body can easily and effectively use
- Producing, breaking down, and regulating hormones in the body
- Converting food into energy and maintaining balanced levels of glucose (a type of sugar), which is your body’s main source of energy
- Removing bilirubin (an orange-yellow material produced when red blood cells are broken down) from the body. Too much bilirubin will cause yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Interesting facts about the liver
Did you know? The liver:

Liver length in healthy term neonates is about as long as a crayon (5.65 cm)

Holds about 13% of your body’s blood at any given moment.

Is the only organ that can completely regenerate (with only 25% healthy tissue).

Was successfully transplanted in a human for the first time in 1967.

May not show signs of serious issues, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, in the early stages.

Is part of the hepatic system, which comes from the Greek word "hepar."
How PBD-ZSD affects the liver
PBD-ZSD is a rare, genetic condition caused by the loss of peroxisome function. Peroxisomes are important parts of cells in the body that are responsible for many key metabolic functions including helping the liver function correctly.
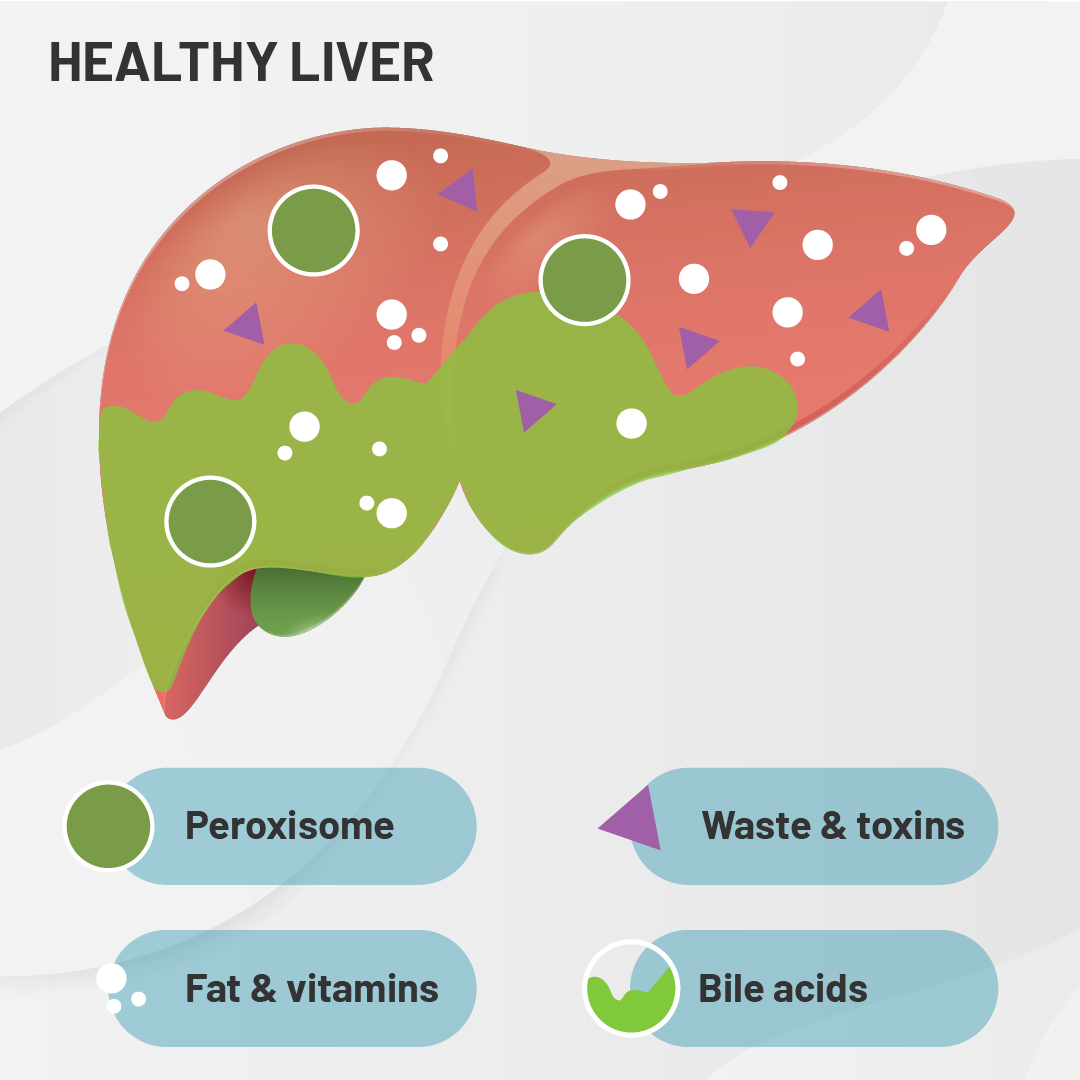
Peroxisomes are in charge of producing bile acids that process fats and nutrients from food and eliminate waste from the body.
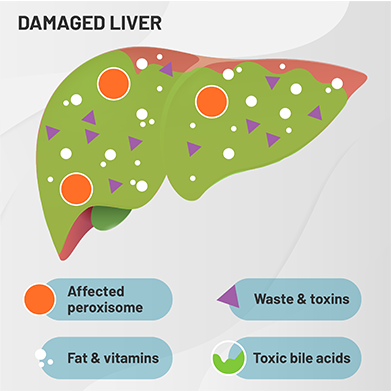
In people with PBD-ZSD, these peroxisomes only partially work or do not work at all. This results in the buildup of abnormal bile acids that can become toxic or harmful to the liver.
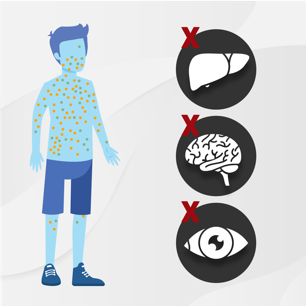
These important parts of cells are needed throughout the body, so if they are not working correctly, multiple organs and body systems can be negatively affected.
While PBD-ZSD can range from mild to moderate or severe, liver dysfunction is almost universal with the disease. Symptoms of PBD-ZSD vary from person to person depending on the age in which symptoms first appear, how many functioning peroxisomes a person has, and which organs are affected.
No 2 people experience the same symptoms. Therefore, it is important to recognize which symptoms are personally affecting your child, including if or when the liver becomes involved.
Monitoring liver function
When your child has PBD-ZSD, monitoring the liver might not seem urgent in the face of noticeably serious issues, like seizures or hearing loss, but a healthy liver is so important that we can’t live without it. Your doctor can assess your child’s liver health by running some important tests.
Liver function test (LFTs)
- A common series of tests that look at levels of different enzymes in the blood
Atypical bile acid test
- A less routine test that identifies high levels of abnormal (or atypical) bile acids in the blood serum, which may indicate potential involvement of the liver

PBD-ZSD Liver Symptom Checker
Identifying symptoms of liver involvement
Take a few minutes to answer the following questions about your child's liver health in relation to PBD-ZSD. Based on your answers, you can access a personalized Discussion Guide to help you talk to your child's doctor about PBD-ZSD and any necessary testing for liver involvement in your child.


Free liver test for diagnosed PBD-ZSD patients
If your child has been diagnosed with PBD-ZSD, your child’s doctor can run a blood test called an atypical bile acid test to determine the presence of toxic bile acids that are harmful to the liver.
Even if the results of your child's liver function tests (LFTs) are normal, it is important to consider the impact of harmful levels of bile acids that can only be detected through the atypical bile acid test. This is not a routine test that your child’s doctor has likely done before, but it provides helpful information about the health of your child’s liver. This test is available at no cost to you, or the doctor, and can be ordered through your child’s doctor. Download the atypical bile acid test form and share with your child’s doctor to run this important test.

Supporting you with helpful resources
Take advantage of these educational resources to help you better understand the liver, symptoms of liver involvement, and how to have a productive discussion with your child’s doctor about PBD-ZSD.
COMMUNITY
Global Foundation for Peroxisomal Disorders (GFPD)
If you have a child with PBD-ZSD, the GFPD provides support and community to families, information on research, scientific papers, and sponsors family and scientific conferences. Connect with other PBD-ZSD families at www.thegfpd.org. View a video of a GFPD-sponsored webinar below to learn more about the impact of PBD-ZSD on liver health.
OTHER USERFUL LINKS
Understanding PBD-ZSD

Understanding PBD-ZSD provides a wealth of resources for patients and caregivers, Learn more about PBD-ZSD, how it is managed, and explore additional resources.
Visit site
Zellweger Spectrum Disorder Stories

YouTube Channel Zellweger Spectrum Disorder Stories YouTube Channel is dedicated to providing clear and engaging videos about PBD-ZSD.
Visit site
ZSD Alliance

The Zellweger Spectrum Disorder Alliance comprises a dedicated tear of physician specialists focused on managing and improving the care of patients with peroxisomal biogenesis disorder Zellweger spectrum disorder or PBD-ZSD.
Visit site
EDUCATION

Liver Fact Sheet
Learn about important liver facts and PBD-ZSD symptoms with this quick reference guide.

Free Liver Test Information
Get information about the free atypical bile acid testing program.
PBD-ZSD Liver Symptom Checklist and Discussion Guide
Not ready to complete the Symptom Checker? You can download this version to fill out later and share at your child's doctor's visit.
FAMILY

Liver Caregiver Kit
Want all your information in one place? This kit includes the previously mentioned educational materials, along with a Liver Plush Toy and Patient Activity Book, to help your child understand the role of the liver and how PBD-ZSD impacts his or her liver health.


Frequently asked questions
1. What is peroxisomal biogenesis disorder-Zellweger spectrum disorder (PBD-ZSD)?
Peroxisomal biogenesis disorder-Zellweger spectrum disorder (PBD-ZSD) is a group of rare, genetic disorders, characterized by the loss of peroxisome function.
Peroxisomes are an important part of the cell and play a key role in producing bile acids, which help break down fats and eliminate waste from the body.
In people with PBD-ZSD, these peroxisomes only partially work or do not work at all. This can result in the buildup of abnormal bile acids that can become toxic to the liver and negatively impact multiple parts of the body.
2. How does PBD-ZSD affect the liver and bile acid production?
PBD-ZSD is caused by a defect in the PEX gene family (the set of genes that controls peroxisomes), which leads to less or no peroxisome function. Functioning peroxisomes help produce bile acids, which are important to help the liver function correctly and eliminate waste from the body.
Bile helps the body:
- Absorb dietary fats, fat-soluble vitamins, and other nutrients.
- Get rid of excess cholesterol, waste, and toxins.
In PBD-ZSD, non-working peroxisomes cannot produce healthy bile acids. Instead, toxic bile acids get trapped in the liver, cause damage, and the liver cannot function properly.
Two key bile acids necessary for proper digestion, absorption, and toxin removal are:
- Cholic acid
- Chenodeoxycholic acid
3. What signs or liver symptoms of PBD-ZSD should I watch for?
One of the most common symptoms of PBD-ZSD is prolonged jaundice—a yellowish color to the skin or white part of the eyes—that lasts more than 2 weeks.
Other signs and symptoms of liver involvement include:
- Poor growth
- Vitamin deficiencies (a lack of vitamins A, D, E, K)
- Pale, foul-smelling stool
- Dark urine
- Enlarged liver or spleen
- Liver dysfunction
4. Who should I talk to if I think my child’s liver is affected by PBD-ZSD?
It’s best to speak with a hepatologist or gastroenterologist if you suspect your child’s liver may be affected by PBD-ZSD. These doctors are responsible for monitoring liver function and any nutrition or feeding difficulties.
5. Is there a way to detect if my child’s liver is affected by PBD-ZSD?
Your child’s hepatologist or gastroenterologist can measure your child’s liver chemistries, including performing certain blood tests to help assess the health of your child’s liver.
They can also run another important but less common blood test called an atypical bile acid test to detect the presence of atypical bile acids (DHCA and THCA) that are harmful to the liver.
6. Is treatment available if my child's liver is affected by PBD-ZSD?
There is an FDA-approved treatment available to help protect the liver in patients with PBD-ZSD.
7. Where can I get more information or support?
The Global Foundation for Peroxisomal Disorders (GFPD) provides support and community to PBD-ZSD families, information on research and scientific papers, and sponsors family and scientific conferences. Learn more at www.thegfpd.org.
Understanding PBD-ZSD.com provides useful information about what to look for and how PBD-ZSD is monitored; it includes a link to recommended guidelines for your doctor to review. Learn more at www.understandingpbd-zsd.com.
